This case study has been submitted for publication at the 7th International Conference on Computational Models of Argument.
A link to the final version of the paper will be published as soon as it becomes available.
An example implementation using MDEOptimiser can be found in this repository.
Introduction
Persuasion is the task of inducing the acceptance of a belief in other agents. A political speech is an example of persuasion, in which the politician attempts to persuade the public that their party is the one to vote for at the next election.
In this case study we show a one-to-many persuasion setting, where a single persuader broadcasts arguments to a multi-party audience with the aim of convincing them of some goal argument. Since each individual audience member reasons with its own set of personal knowledge (which we assume is known to the persuader) any particular set of persuader arguments may be convincing to some audience members but not others, and so the persuader must carefully select which arguments it should assert in order to maximise the number of audience members it convinces.
This is a challenging problem because of the number of potential solutions and the number of audience members to evaluate against: to exhaustively explore the solution space, for each subset of the persuader’s arguments one must consider each audience member and determine whether it would be convinced by those arguments.
To efficiently determine the arguments the persuader should assert, i.e., its strategy, we specify the problem using search-based model engineering.
By representing the persuasion setting as a meta-model (a schema describing the structure of valid solutions), we can apply evolutionary search to a find a near-optimal strategy for the persuader that maximises the number of convinced audience members.
Implementation
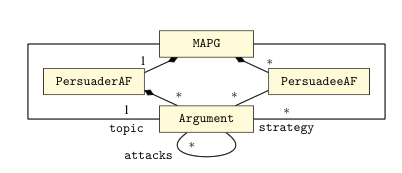
In the figure above, we show a metamodel of this problem. The goal of this problem is to find a strategy that is effective and efficient. We have specified this problem both as a single-objective and multi-objective problem.
In the single-objective case we are only measuring the effectiveness. While in the multi-objective case we are measuring both effecitiveness and efficiency.
In the figure below, we show an implementation of the case study using our DSL.