This case study has been presented at the Transformation Tool Contest 2016 workshop.
A link to the final version of the paper with our solution presented there can be found here.
An example implementation using MDEOptimiser can be found in this repository.
Introduction
The Class Responsibility Assignment (CRA) case study has been introduced at the 2016 Transformation Tool Contest. The problem that has to be solved comes from the software engineering field. The goal of this problem is to transform a procedural software application to an object oriented architecture while maintaining good cohesion and coupling. The quality of the produced solutions is measured using the CRA index, as a single objective. The problem supplies a responsibility dependency graph, that contains a set of functions and attributes with dependencies between them. In the metamodel, these entities are instances of the abstract type Feature.
The CRA case study authors provide a set of five input models. The difference between them is the number of Features present. Input model A, is the smallest model with only nine features. The largest model provided is model E with 160 features. Across all models, each set of features has an increasing number of dependencies between them. A summary of all the input models is included in the table below.
| Model A | Model B | Model C | Model D | Model E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attributes | 5 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 |
| Methods | 4 | 8 | 15 | 40 | 80 |
| Data Dep. | 8 | 15 | 50 | 150 | 300 |
| Functional Dep. | 6 | 15 | 50 | 150 | 300 |
Implementation
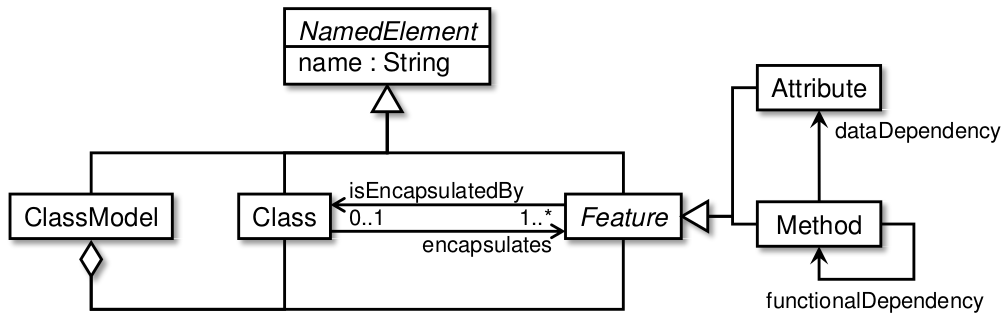
In the figure above, we show a metamodel of this problem.
To find a solution, the user is required to create Classes in the ClassModel and assign Features to them such that: all Features are assigned to a Class; the model with the highest CRA index value is found. The problem has an additional constraint requiring that each Feature is assigned to only one Class at a time. We have specified this problem with a single objective:
1. [Objective 1] maximise the CRA index.
The problem also has one constraint:
1. [Constraint 1] all Features must be encapsulated in a Class.
In the figure below we show an implementation of the case study using our DSL.
In our implementation we have used four mutation operators to explore the search space. These have been implemented using Henshin and are shown in the figure below.
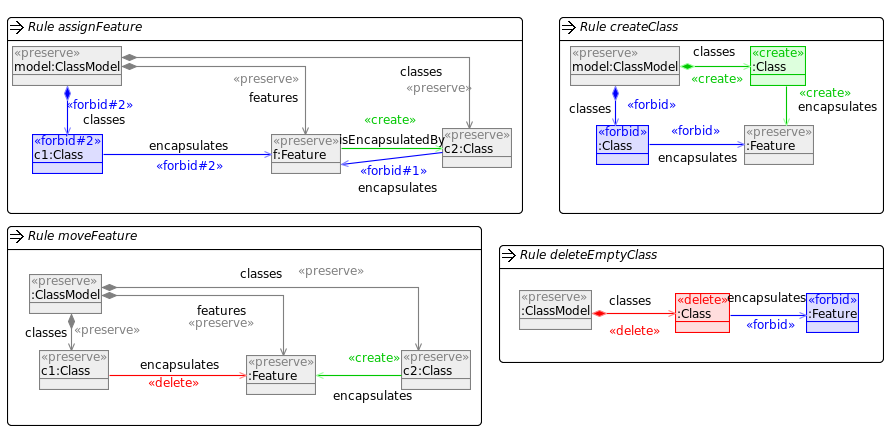
Automatic mutation generation
In the figure below, we include an example of the DSL that allows the user to specify the nodes