This case study has been presented at the Transformation Tool Contest 2018 workshop.
An example implementation using MDEOptimiser can be found here.
Introduction
This case study is a combinatorial problem covering the combined challenge of software-variant selection and component-resource allocation. It posits a domain where a system architecture is comprised of a number of components, some of which can be used to satisfy certain functional requests to the system. For each component there are one or more implementations. Each implementation may require other components as well as making requirements on resources allocated to the implementation. In addition to providing the component’s functional services, the implementations provide different levels of non-functional quality. To express how they do this, implementations use a simplified form of parametrised contracts, expressing their requirements on resource provision and the non-functional properties provided by used components and, in return, promising to provide a certain level of quality.
Implementation
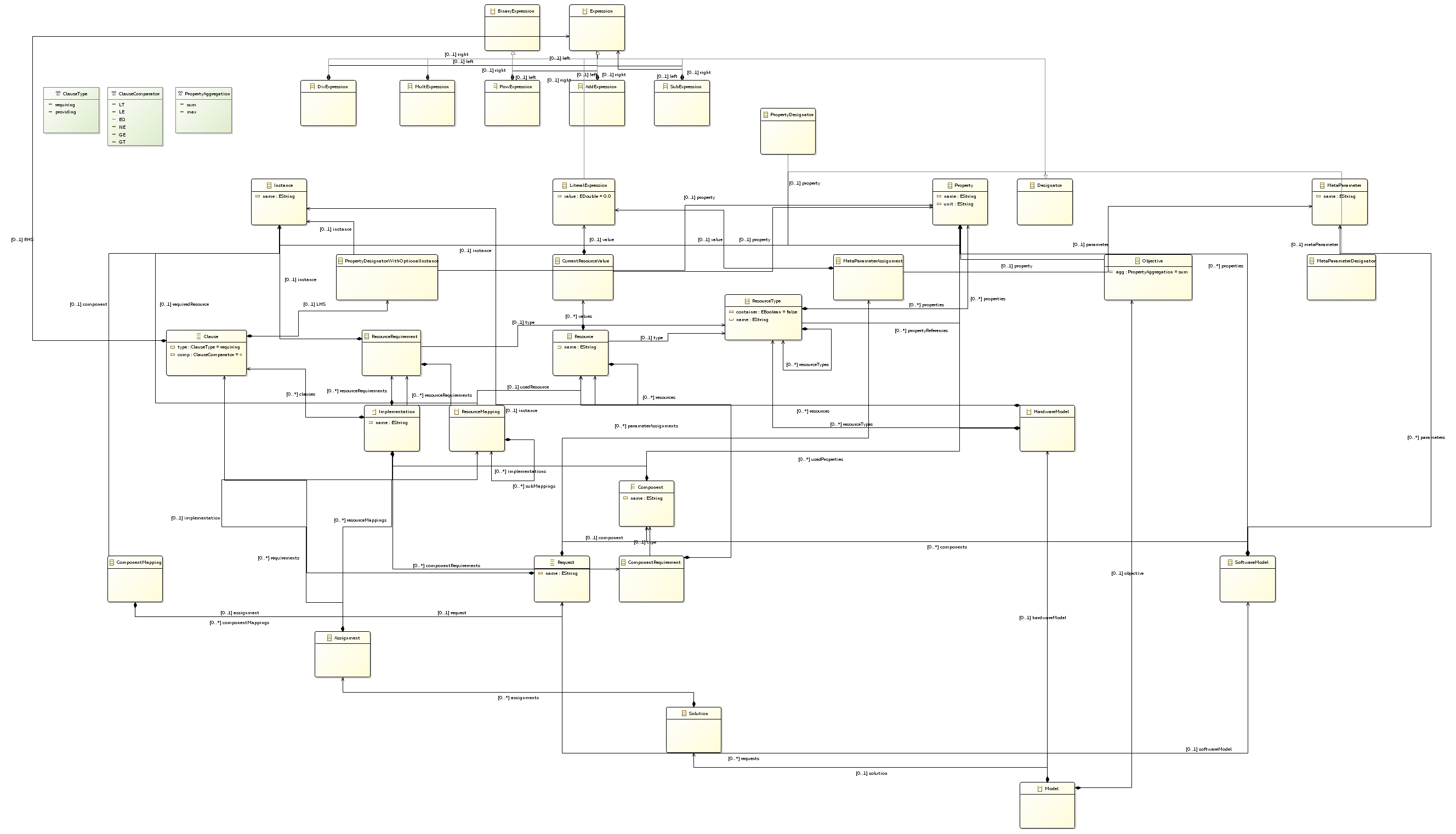
In the figure above, we show a metamodel of this problem. The goal of this problem is to find an optimal selection of implementations and allocation of resources so that a set of requests can be satisfied. Requests consist of a component to be called as well as conditions on the quality properties to be provided by this component. The overall objective is expressed as a single objective either summarising or selecting the maximum value of one specific quality property for all requests in a model.
We have specified this problem using a single objective:
1. [Objective 1] minimise resource allocation objective;
2. [Objective 2] minimise the non-functional requirements violations by depending implementations;
The problem has the following constraints:
1. [Constraint 1] Ensure that all requests are mapped to an implementation;
2. [Constraint 2] Ensure that each component has one implementation only;
3. [Constraint 3] Ensure that each resource is only mapped once;
4. [Constraint 4] Ensure that the request non functional properties are provided by the selected components;
5. [Constraint 5] Ensure that all the request required compoentns are implemented;
In the figure below we show an implementation of the case study using our DSL.
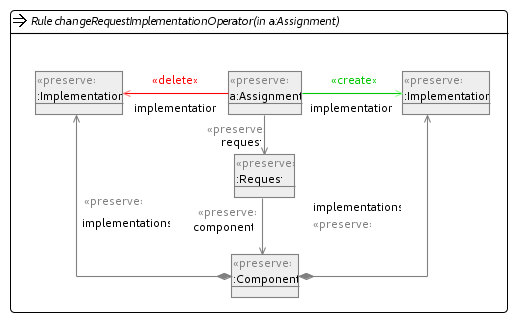
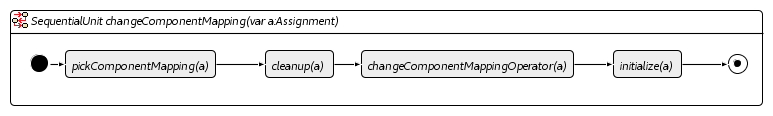
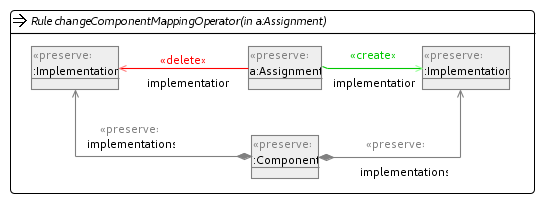
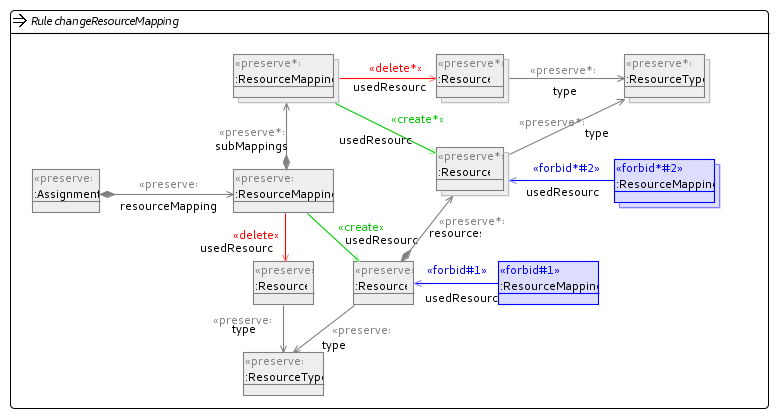
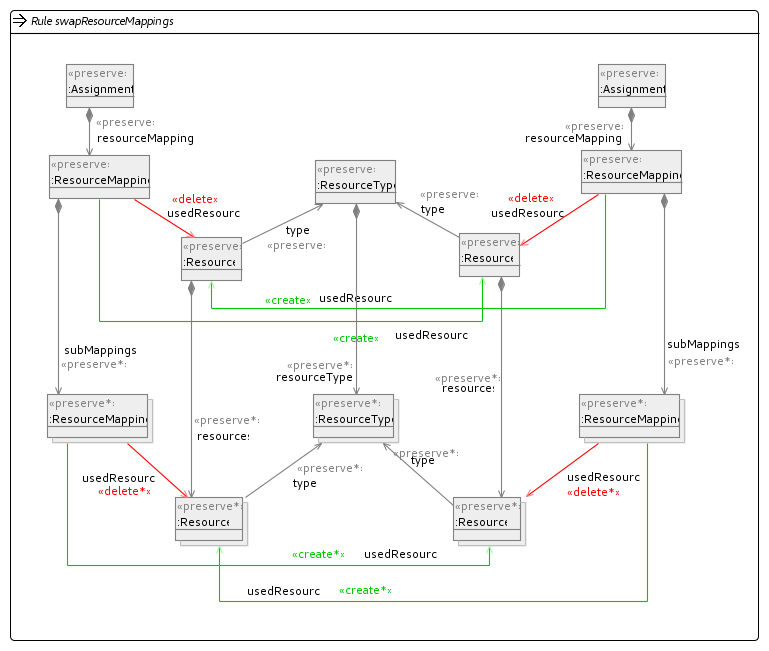
In our implementation we have used four mutation operators to explore the search space. These have been implemented using Henshin and are shown in the figures below.
Change Request Implementation Operator
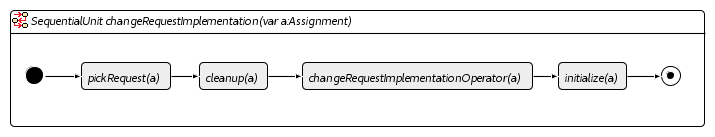
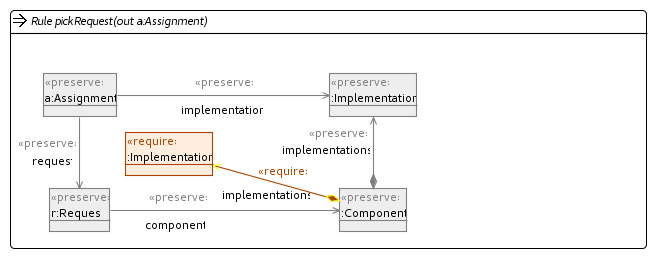
Change Component Mapping Operator
Change Resource Mapping Operator
Swap Resource Mapping Operator
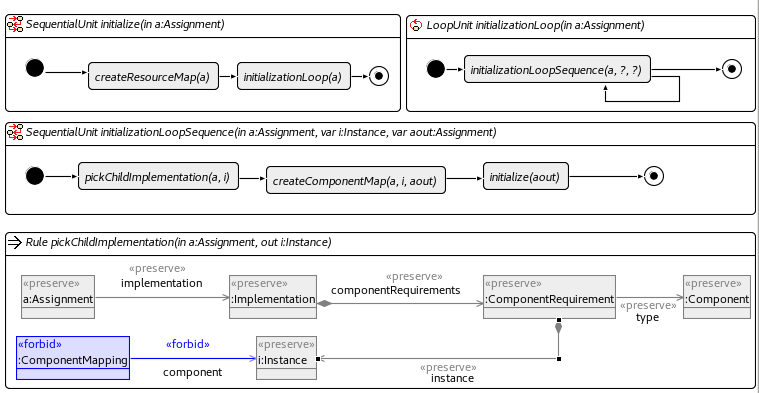
Model initialisation
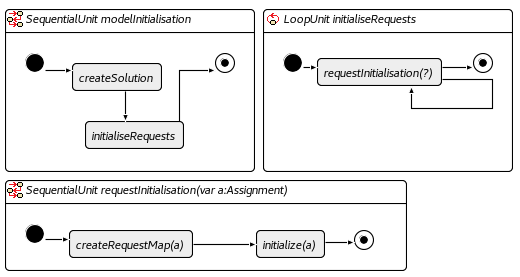
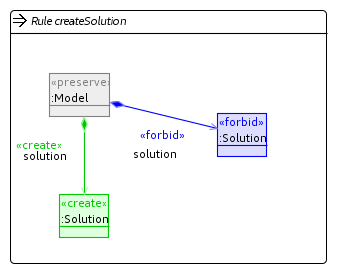
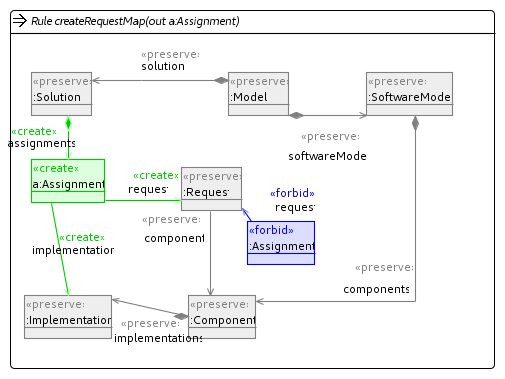
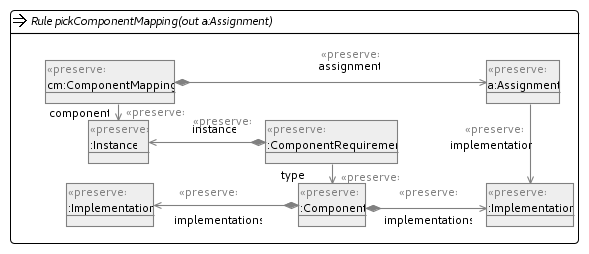
Common operators
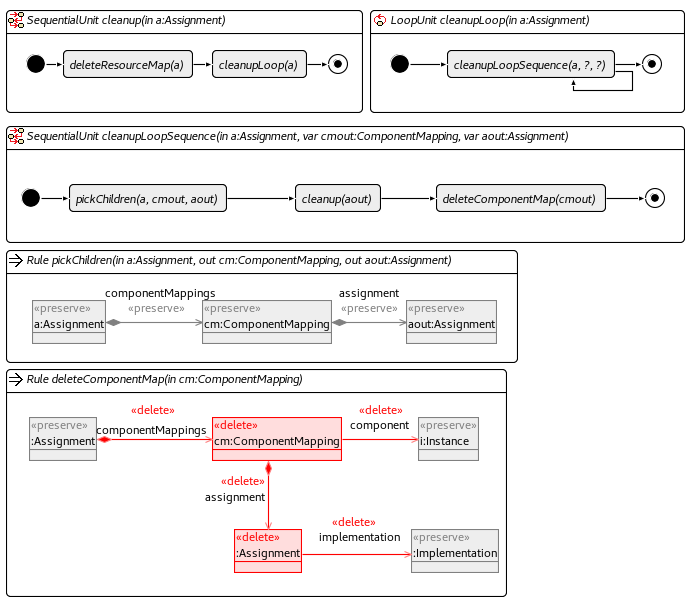
These operators are rules or units that are reused by other operators in our implementation.
Initialisation Unit
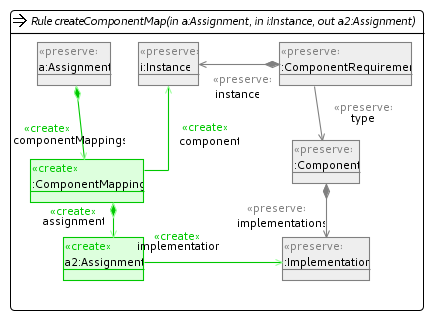
Cleanup Unit